Mediterranean Diet Linked to Lower Stress and Improved Mood, Research Shows
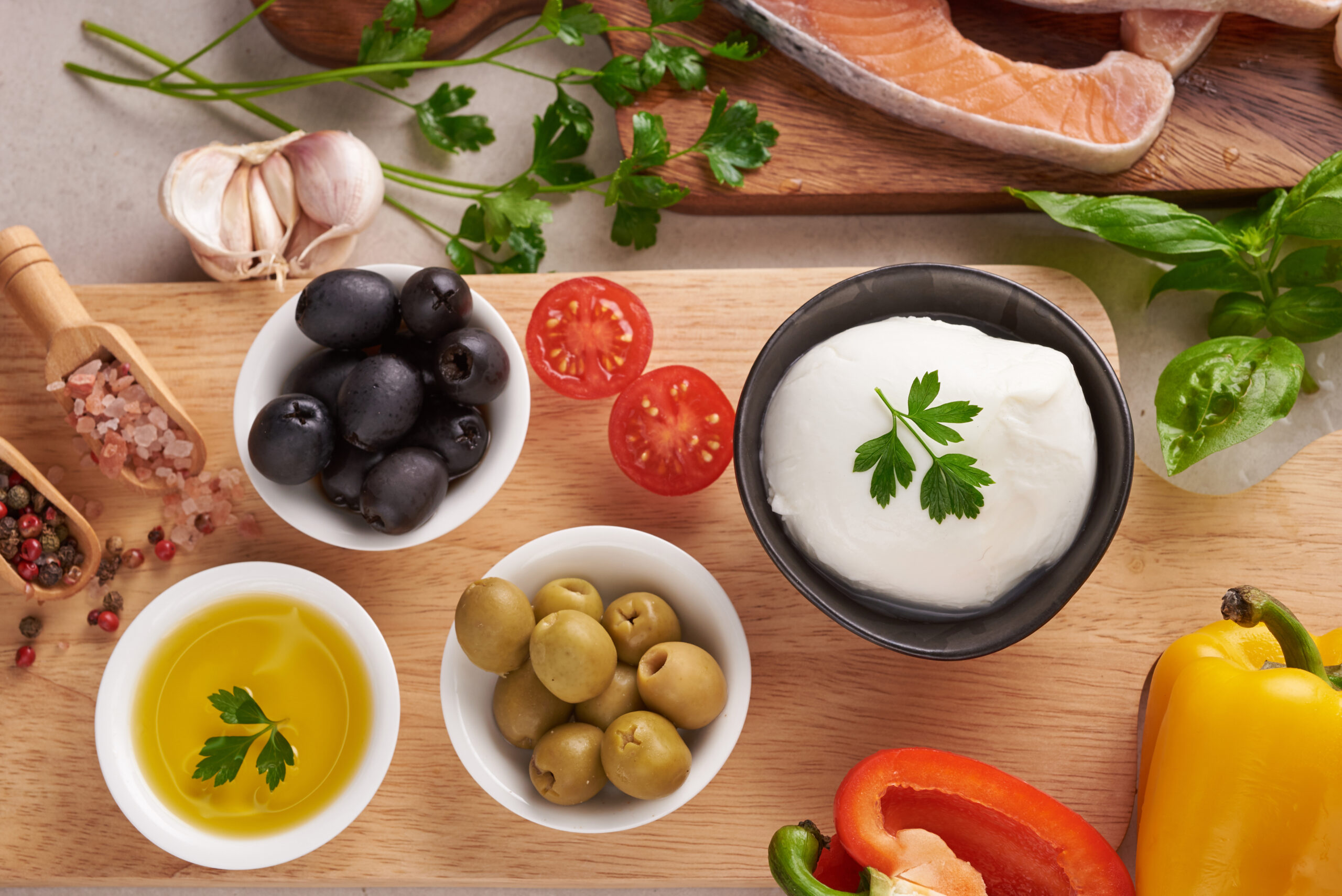

New research suggests the Mediterranean diet helps reduce stress and improve mood. The study, which focused on participants primarily aged 18-29, found a significant correlation between the diet and decreased feelings of mental distress. The findings are supported by comprehensive studies involving millions of participants, highlighting the diet’s potential benefits.
The Mediterranean diet is widely acclaimed for its health benefits, emphasizing lean protein, fresh fruits, vegetables, and limited alcohol intake. According to Alyssa Kwan, MS, RD, “These are all anti-inflammatory; we understand that there are positive benefits of an anti-inflammatory diet due to the gut-brain axis.”
Dark leafy greens, a staple in the Mediterranean diet, were inversely correlated with feelings of stress according to the Kessler Scale. Foods like white meat, eggs, and red meat also contributed to reduced stress and increased positive feelings such as confidence.
Experts like Lina Begdache, PhD, RDN, emphasize the importance of a balanced diet for mental well-being. “Our results showed that the Mediterranean diet reduced feelings of distress as well as increased feelings of eustress [positive stress],” says Begdache. This aligns with other research linking the diet to lower rates of depression and anxiety.
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in this connection. “Remember that 95% of your serotonin is coming from your gut,” notes Eva Selhub, MD. Serotonin stability is crucial for mental health, and blood sugar fluctuations can disrupt this balance. “Blood sugar fluctuations are the main cause of mental distress and the stress response because serotonin levels become unstable,” explains Begdache.
A 2022 meta-analysis involving over 10 million participants and over 200,000 cases of atrial fibrillation (AFib) found that lifestyle factors like diet significantly impact health outcomes. While the Mediterranean diet shows promise in reducing stress, other studies highlight risks associated with unhealthy habits. For example, having one alcoholic drink per day increases AFib risk by 6%.
Additionally, tobacco smoking has been shown to increase AFib risk, according to a 2020 systematic review and meta-analysis. These findings underscore the importance of dietary choices and lifestyle in managing overall health.
Kristin Kirkpatrick, MS, RD, advises making gradual changes to adopt a Mediterranean dietary pattern. “Start with foods you love from a Mediterranean pattern while reducing ultra-processed and empty-calorie foods,” she suggests. Simple swaps like choosing whole grain bread over white bread or opting for fruits and healthy fats as snacks can make a significant difference.
Eva Selhub also recommends adding color to one’s plate. “Think about adding color to your plate: plants, vegetables, fruits, nuts and seeds, lean proteins, healthy grains, and fatty fish,” she advises.
The Perceived Stress Scale (PSS), used since 1983 to measure stress levels, continues to be an essential tool in evaluating how dietary patterns affect mental health. By incorporating healthy foods and reducing harmful habits like excessive alcohol consumption and smoking, individuals can potentially improve their stress levels and overall well-being.
Adopting a Mediterranean diet may offer significant benefits for reducing stress and improving mood. This research adds to a growing body of evidence supporting the positive effects of dietary choices on mental health.
Parts of this article has been sourced by Healthline and fact-checked by Jennifer Chesak, MSJ
Featured Image by jcomp on Freepik




Leave a Reply